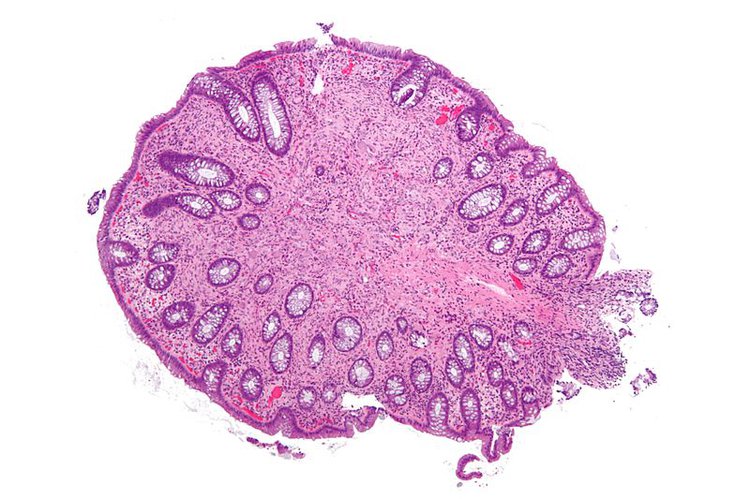
What Is Ganglioneuroma
It is also known as ganglioma. Ganglioneuroma is a benign non-cancerous tumor made up of mature ganglion and nerve sheath cells.
 Terminology And Morphologic Criteria Of Neuroblastic Tumors Shimada 1999 Cancer Wiley Online Library
Terminology And Morphologic Criteria Of Neuroblastic Tumors Shimada 1999 Cancer Wiley Online Library
There are no immature neuroblastic elements.
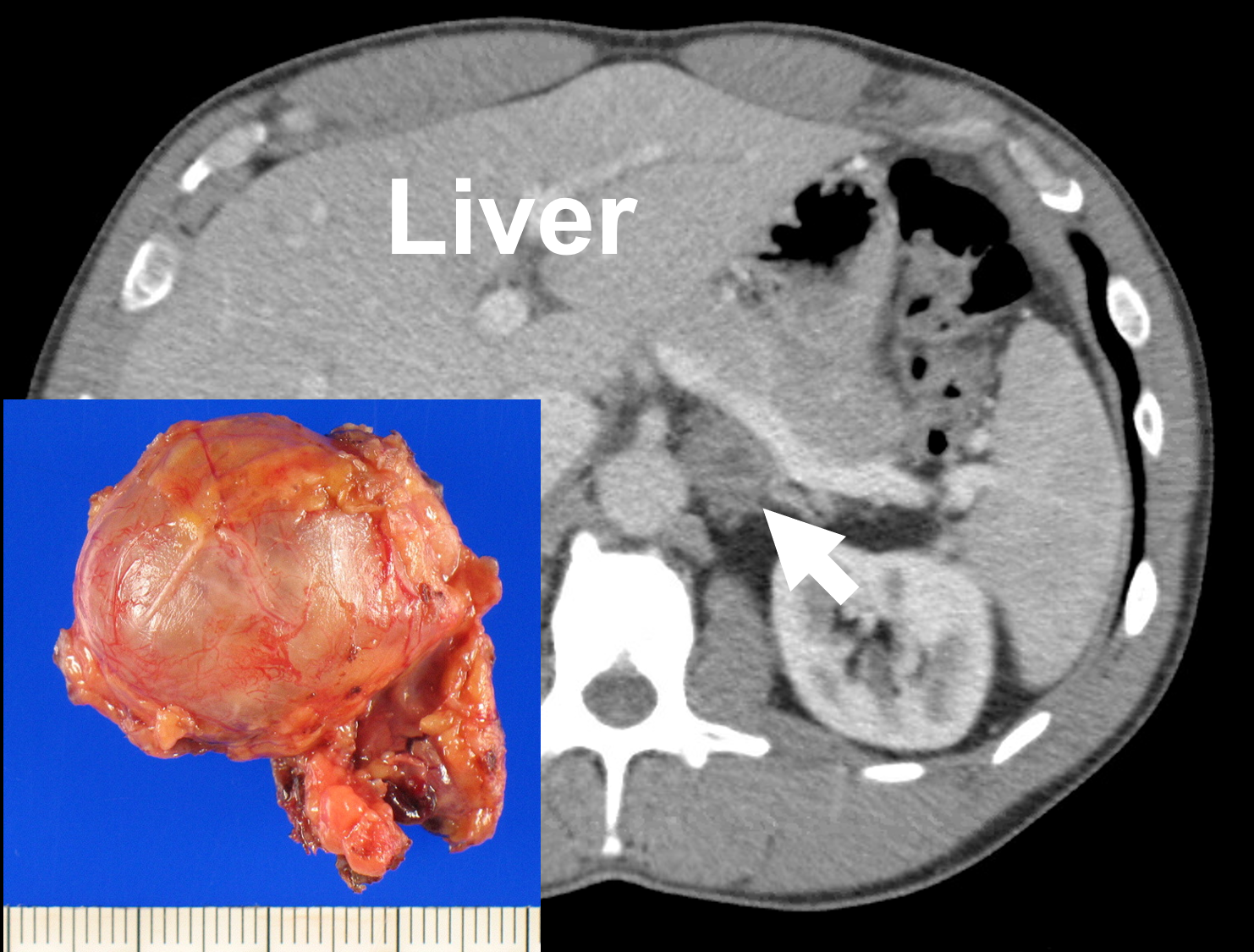
What is ganglioneuroma. An intermediate tumor is one that is between benign slow-growing and unlikely to spread and malignant fast-growing aggressive and likely to spread. Autonomic nerves manage body functions such as blood pressure heart rate sweating bowel and bladder emptying and digestion. Mature benign neoplasm that originates from neural crest cells of sympathetic ganglia or adrenal medulla.
A benign neoplasm composed of mature ganglionic neurons scattered singly or in clumps within a relatively abundant and dense stroma of neurofibrils and collagenous fibersgangliocytoma ganglioma neurocytoma. Ganglioneuroblastoma is an intermediate tumor that arises from nerve tissues. On imaging usually they present as well-defined solid masses and can be quite large at presentation.
These tumors are most commonly identified during an examination for an unrelated medical condition although they do sometimes lead to symptoms causing a doctor to identify them while seeking the cause of the symptoms. The tumors are usually noncancerous benign. Removal is usually the only treatment necessary.
Neuroblastoma ganglioneuroblastoma ganglioneuroma. The tumors are usually noncancerous benign. Ganglioneuromas usually occur in people over 10 years of age.
Ganglioneuromas of the intestinal tract are considerably less common. Ganglioneuroma is a benign neuroblasic tumour. It is often asymptomatic and may be diagnosed by serendipity.
Mimicking an ovarian mass in a child. They most commonly arise in the posterior mediastinum and the retroperitoneum. Ganglioneuroma is a benign neuroectodermal tumor composed of ganglion and Schwann cells.
A ganglioneuroma is an unusual and usually benign tumor found in the peripheral nervous system. Removal is usually the only treatment necessary. Ganglioneuromas are fully differentiated neuronal tumors that do not contain immature elements and potentially occur anywhere along with the peripheral autonomic ganglion sites.
Ganglioneuroma of Colon is a rare benign non-cancerous lesion that forms in the colon large intestine. Autonomic nerves manage body functions such as blood pressure heart rate sweating bowel and bladder emptying and digestion. Neuroblastoma ganglioneuroblastoma and ganglioneuroma.
On a spectrum from least most differentiated. Surgical removal is the treatment of choice. Ganglioneuroma are rare benign neural tumor of sympathetic nervous system originating from neural crest sympathogonia.
Ganglioneuroma GN is a benign differentiated variety of neurogenic tumor. However ganglioneuromas themselves are fully differentiated neuronal tumors that do not contain immature elements. It commonly occurs in the chest posterior mediastinum abdomen retroperitoneum paraspinal region along the spinal cord region and the adrenal gland.
Ganglioneuroma is a very rare benign non-cancerous neuroblastic tumor of neural crest origin made up of mature ganglion and nerve sheath cells and arise wherever sympathetic nerves or sympathetic nervous tissue exist 1. There are 3 kinds of histopathological patterns of neuroblastic tumours. Ganglioneuroma tumor usually appears in areas with large vessels in the course of the trunk of the sympathetic system 2.
Ganglioneuromas are benign tumors composed of a proliferation of nerve fibers Schwann cells and ganglion cells. Ganglioneuroma is a rare and benign tumor of the autonomic nerve fibers arising from neural crest sympathogonia which are completely undifferentiated cells of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglioneuromas usually occur in people over 10 years of age.
Stage L1L2 with ganglioneuroma maturing or ganglioneuroblastoma intermixed histology. Ganglioneuroma is a rare tumor that develops in a special type of nerve cells the neural crest belonging to the sympathetic nervous system autonomic. Ganglioneuromas are rare tumors that most often start in autonomic nerve cells.
Ganglioneuromas are not pre-malignant - meaning that individuals are not at an increased risk for developing colon cancer It can occur in middle-aged and older men and women aged around 50 years. Ganglioneuroblastoma is a tumor that has both malignant and benign parts. It should not to be confused with ganglioglioma.
The most common sites of involvement are along the distribution of sympathetic nervous system and include posterior mediastinum retroperitoneum and adrenal gland. However it has been suggested that postoperative complications and sequelae might outweigh the benefits of this approach. Ganglioneuromas are rare tumors that most often start in autonomic nerve cells.
Ganglioneuromas are benign tumors of mature ganglion and nerve sheaths.
Ganglioneuroma Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials
 Rare And Uncommon Adrenal Diseases And Tumors
Rare And Uncommon Adrenal Diseases And Tumors
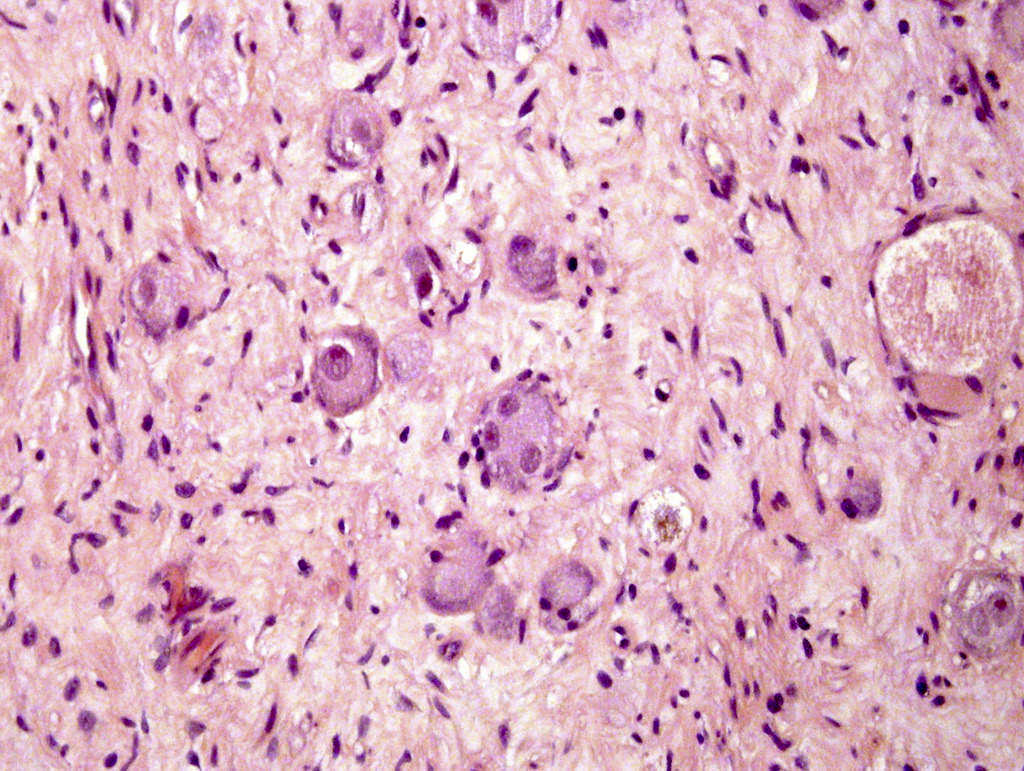 Pathology Outlines Ganglioneuroma
Pathology Outlines Ganglioneuroma
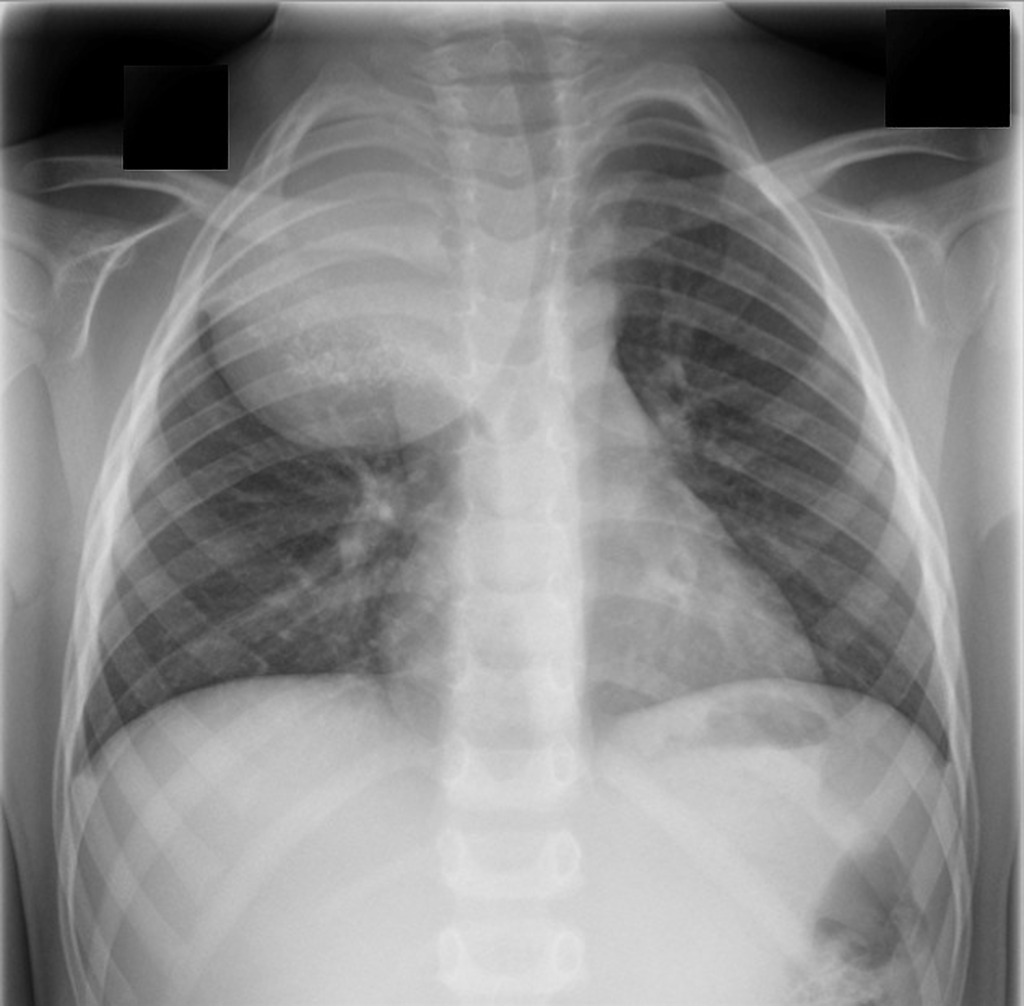 Ganglioneuroma Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Ganglioneuroma Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
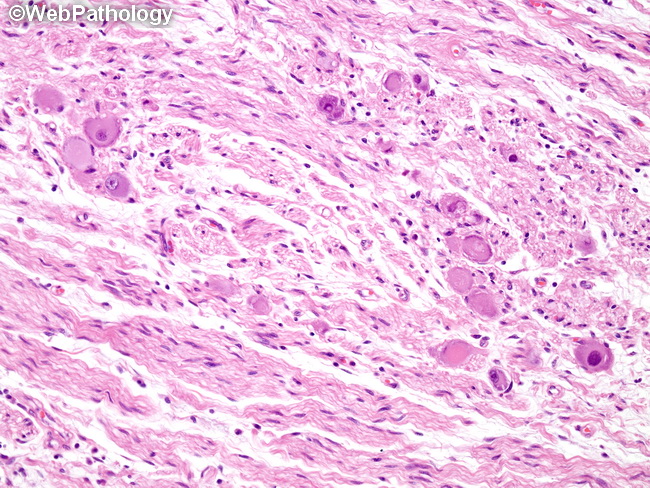 Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
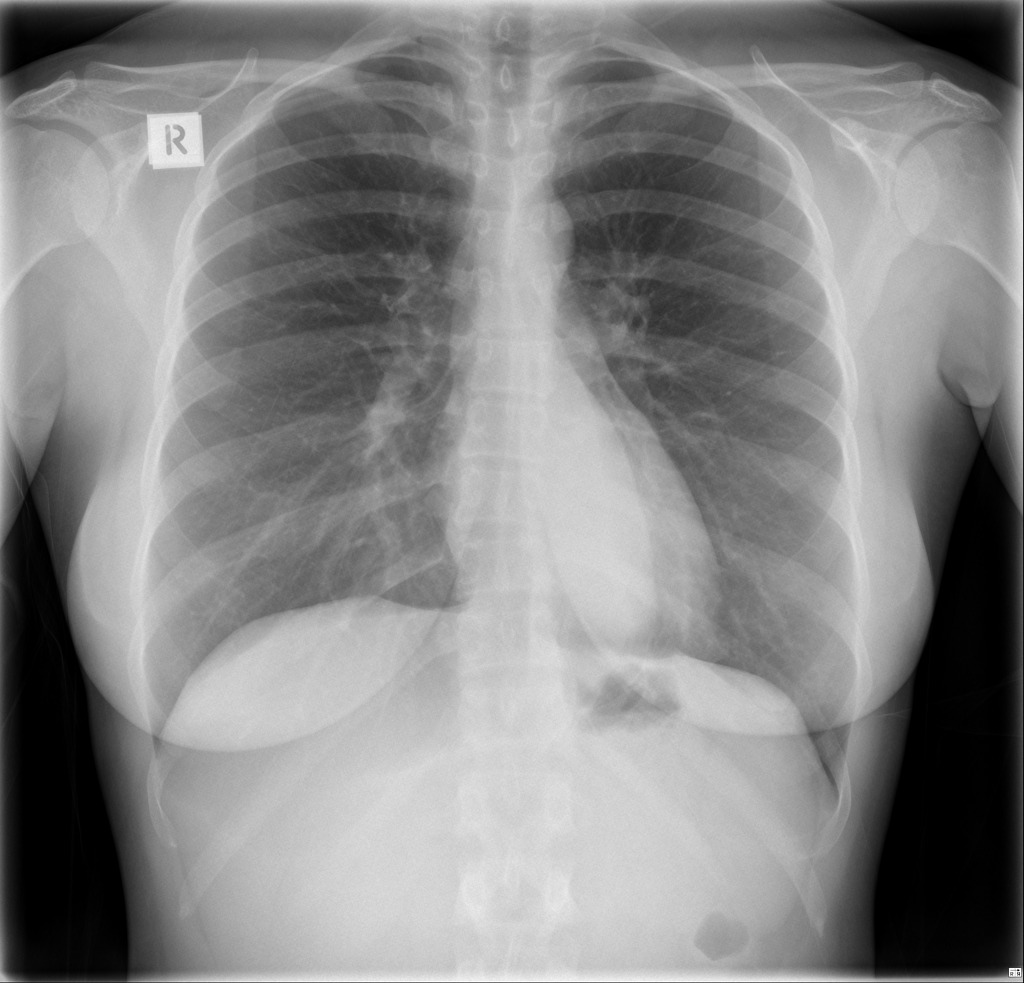 Ganglioneuroma Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Ganglioneuroma Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
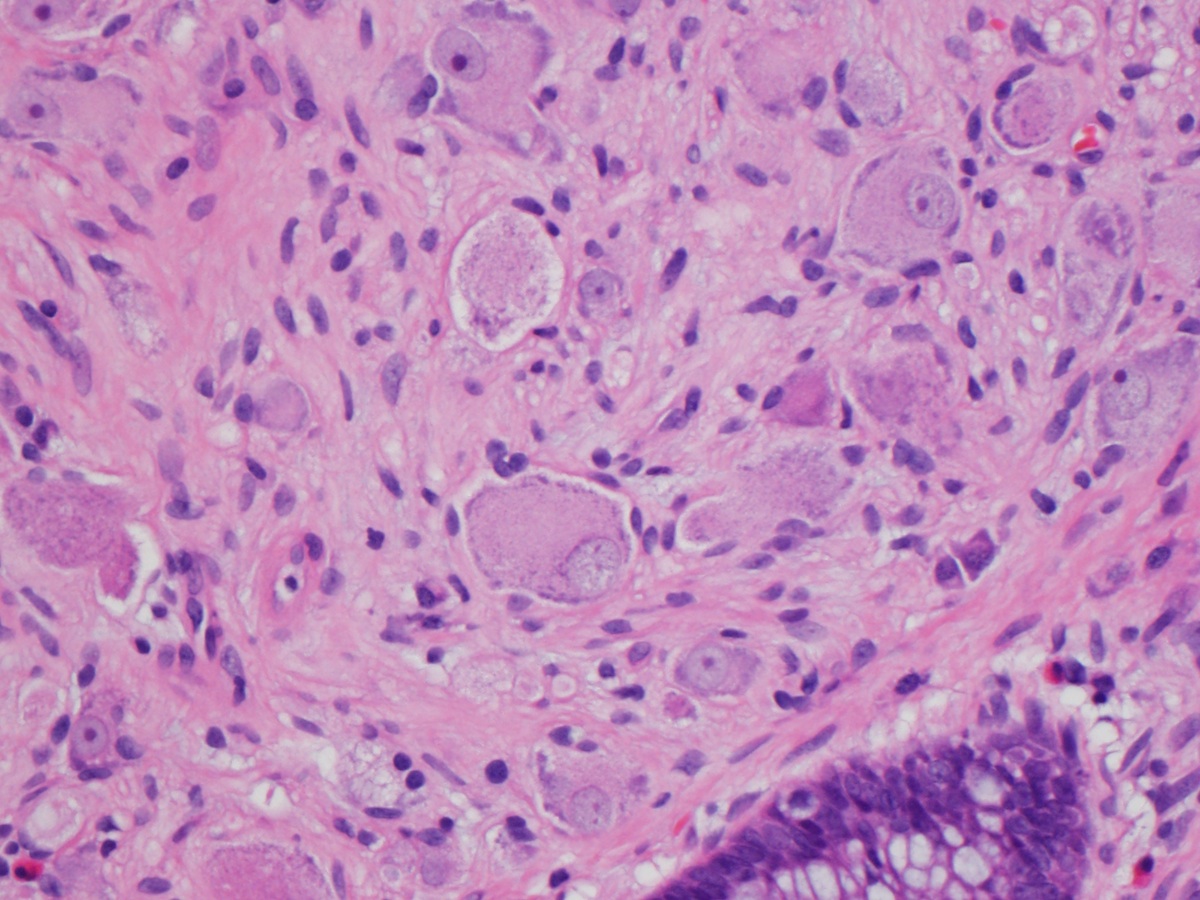 Pathology Outlines Ganglioneuroma
Pathology Outlines Ganglioneuroma
 Pdf Retroperitoneal Ganglioneuroma In Childhood A Presentation Of Two Cases
Pdf Retroperitoneal Ganglioneuroma In Childhood A Presentation Of Two Cases
 Ganglioneuroma An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ganglioneuroma An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Ganglioneuroma Of The Adrenal Gland And Retroperitoneum A Report Of Unusual Case And Review Of The Literature Sages Abstract Archives
Ganglioneuroma Of The Adrenal Gland And Retroperitoneum A Report Of Unusual Case And Review Of The Literature Sages Abstract Archives
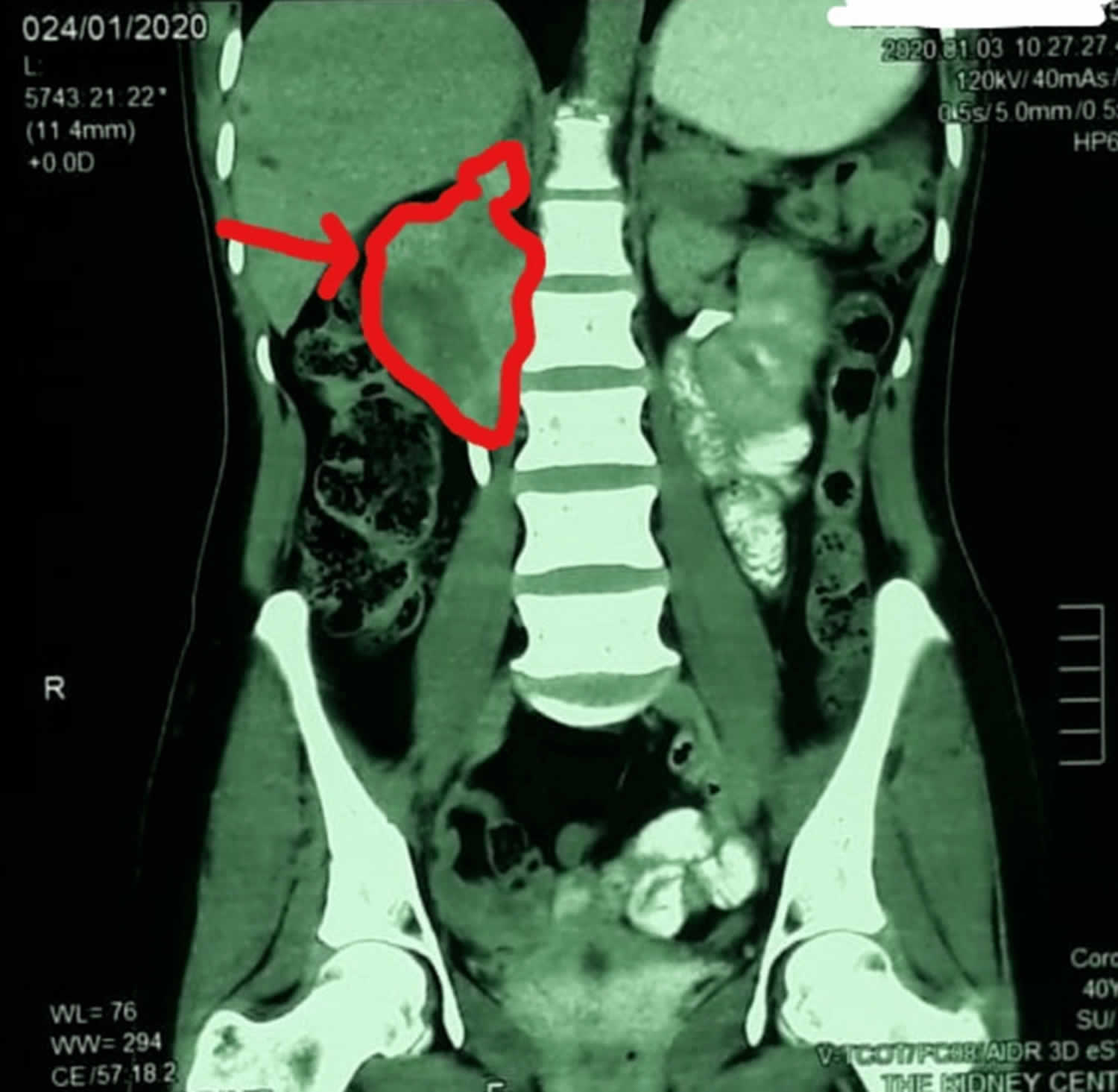 Ganglioneuroma Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis
Ganglioneuroma Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis
 Ganglioneuroma Of Mediastinum And Adrenal Gland Sciencedirect
Ganglioneuroma Of Mediastinum And Adrenal Gland Sciencedirect
 Ganglioneuroma Multiple Surgeons Take On Multiple Tumors
Ganglioneuroma Multiple Surgeons Take On Multiple Tumors
 Ganglioneuroma Of The Adrenal Gland Semantic Scholar
Ganglioneuroma Of The Adrenal Gland Semantic Scholar
 Ganglioneuroma Regina Leader Post
Ganglioneuroma Regina Leader Post
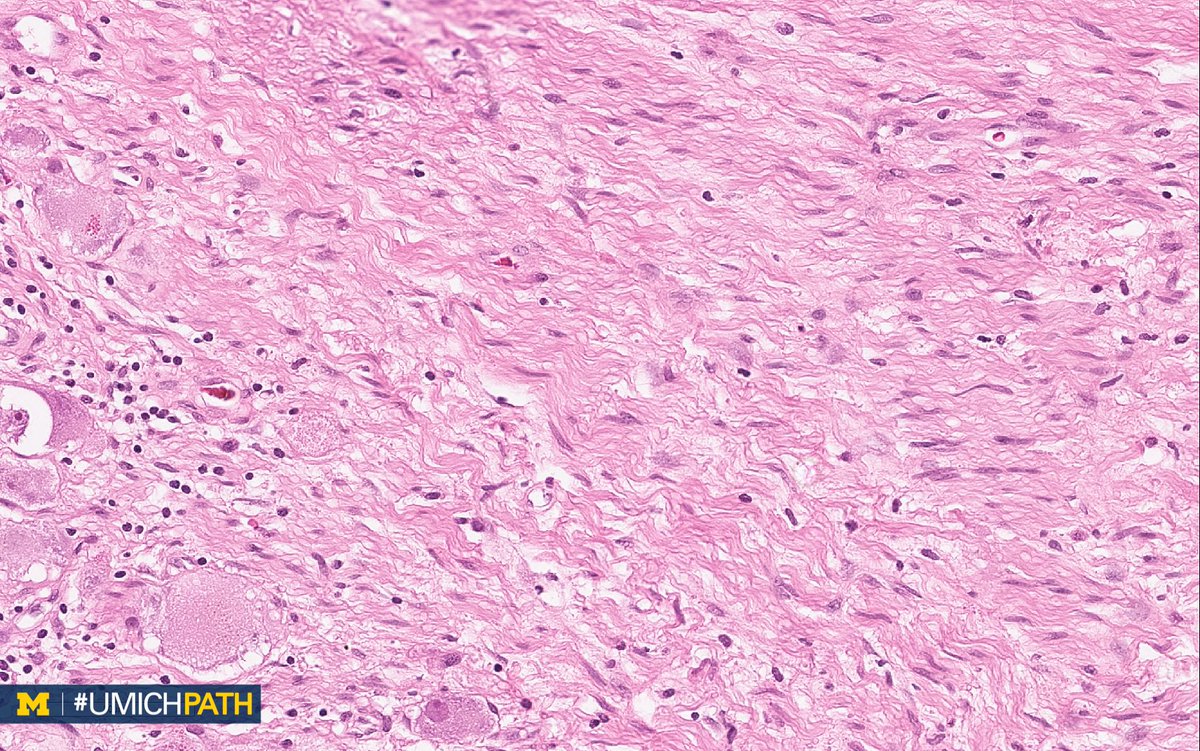 Michigan Pathology On Twitter A Ganglioneuroma Benign Posterior Mediastinum Histo Encapsulated Mass Of Spindled Cells W Schwannian Stroma W Clusters Of Mature Ganglion Cells Patchy Lymphocytic Inflammation If Scattered Differentiating
Michigan Pathology On Twitter A Ganglioneuroma Benign Posterior Mediastinum Histo Encapsulated Mass Of Spindled Cells W Schwannian Stroma W Clusters Of Mature Ganglion Cells Patchy Lymphocytic Inflammation If Scattered Differentiating
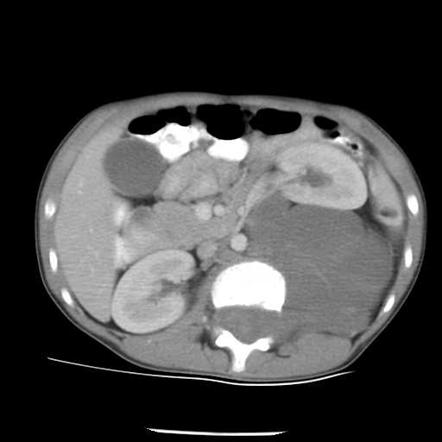 Ganglioneuroma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Ganglioneuroma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org